
What Is Audiology?
Audiology is the study of hearing and hearing-related disorders. An Audiologist is a health care professional who specializes in hearing-related issues. They work to prevent, identify, and assess hearing loss in individuals.
An Audiologist can determine if you can hear within the normal range, and if not, the nature and severity of your hearing loss. To treat your hearing loss, an Audiologist may fit you with a hearing aid or an assistive listening device. Audiologists work with a wide range of clients, from infants to seniors.
What Does An Audiologist Do?
- Administer hearing tests to identify and diagnose hearing issues.
- Assessment of auditory processing disorders (i.e. the ability to listen and process instructions in the presence of noise).
- Aural rehabilitation (i.e. fit clients with and help them use hearing aids, cochlear implants, or assistive listening devices).
- Counsel clients when they need help maintaining, troubleshooting, or getting the most out of their hearing equipment.
- Help clients and their families engage in proven strategies to enhance listening and communication skills.

Risk Factors For Hearing Loss
- Tinnitus: This disorder affects 1 in 5 people, and can be caused by excessive noise exposure, hearing loss, an ear injury, or a circulatory system disorder. 90% of people with tinnitus have hearing loss.
- Cognitive decline: Those with untreated hearing loss experience a 30 to 40% greater decline in thinking abilities, compared to those without hearing loss.
- Poor balance: People with mild hearing loss and 3 times more likely to have a history of falling. Every additional 10 decibels of hearing loss increases the chance of falling by 1.4 times.
- Hypertension: There is a significant association between high blood pressure and untreated hearing loss. Hypertension can also accelerate hearing loss in older adults.
- Obesity: A higher body mass index (BMI) and a larger waist circumference are associated with an increased risk of hearing loss in women.
- Osteoporosis: A study linked osteoporosis and hearing loss, theorizing that demineralization of the three middle ear bones may contribute to a conductive hearing impairment.
- Isolation: Adults 50 years and older with untreated hearing loss are more likely to report depression, anxiety, anger, frustration, emotional instability, and paranoia, compared to those who use hearing aids.
- Depression: Untreated hearing loss contributes to poorer quality of life, isolation, and reduced social activity, which leads to depression.
- Eye health: Vision helps you identify where a sound is coming from. If you have vision and hearing loss, your ability to target sound location is compromised. The amplification from hearing aids helps to compensate for vision loss.
- Heart health: The inner ear is extremely sensitive to blood flow. Studies show that a healthy cardiovascular system (the heart, arteries, and veins) has a positive effect on hearing. Inadequate blood flow and trauma to the blood vessels of the inner ear can contribute to hearing loss.
- Smoking: Current smokers have a 70% higher risk of experiencing hearing loss than non-smokers.
- Diabetes: Hearing loss is twice as common in people with diabetes compared to those without. What’s more, adults with blood glucose levels higher than normal, but not high enough for a diabetes diagnosis, have a 30% higher rate of hearing loss compared to those with normal blood sugar levels.
- Ototoxicity: There are more than 200 medications on the market today that are known to cause hearing loss. These include: aspirin, Quinine, water pills, certain antibiotics, some anticancer drugs, some anaesthetics, and certain environmental chemicals.
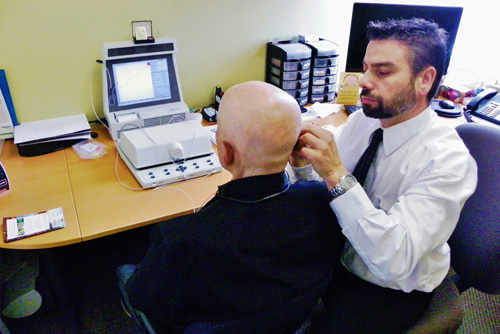
Rui Oliveira, Audiologist, fits a hearing aid
to his client and verifies the settings using
Real Ear Measures.
Do I Need A Hearing Test?
- Do you often ask people to repeat themselves?
- Do you think people mumble or speak too softly?
- Do you often turn up the TV or radio?
- Do you find it difficult to follow conversations in a group setting?
- Do you find it difficult to tell which direction a sound is coming from?
- Do you experience ringing in your ears?
- Do you avoid events that you previously enjoyed because you are embarrassed about not being able to hear clearly or follow conversations?
If you answered “yes” to any of these questions, contact HearSay to book a hearing test with our qualified Audiologist. Discover how the perfect hearing aid can improve the quality of your life.
